Spectrum-optimized direct image reconstruction of super-resolution structured illumination microscopy
doi: 10.1186/s43074-023-00092-6
Spectrum-optimized direct image reconstruction of super-resolution structured illumination microscopy
-
Abstract:
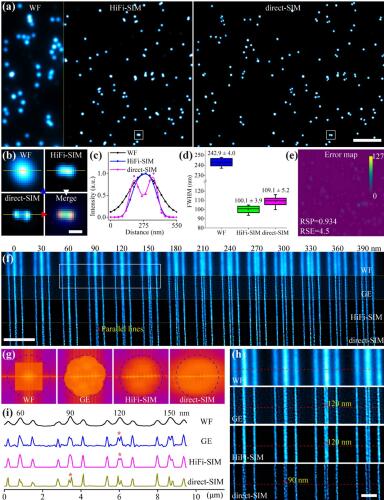
Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy (SR-SIM) has become a widely used nanoscopy technique for rapid, long-term, and multi-color imaging of live cells. Precise but troublesome determination of the illumination pattern parameters is a prerequisite for Wiener-deconvolution-based SR-SIM image reconstruction. Here, we present a direct reconstruction SIM algorithm (direct-SIM) with an initial spatial-domain reconstruction followed by frequency-domain spectrum optimization. Without any prior knowledge of illumination patterns and bypassing the artifact-sensitive Wiener deconvolution procedures, resolution-doubled SR images could be reconstructed by direct-SIM free of common artifacts, even for the raw images with large pattern variance in the field of view (FOV). Direct-SIM can be applied to previously difficult scenarios such as very sparse samples, periodic samples, very small FOV imaging, and stitched large FOV imaging.
-
[1] Gustafsson MGL. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J Microsc. 2000;198(2):82–7. [2] Gustafsson MGL, Shao L, Carlton PM, Wang CJR, Golubovskaya IN, Cande WZ, et al. Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination. Biophys J. 2008;94(12):4957–70. [3] Schermelleh L, Carlton PM, Haase S, Shao L, Winoto L, Kner P, et al. Subdiffraction multicolor imaging of the nuclear periphery with 3D structured illumination microscopy. Science. 2008;320(5881):1332–6. [4] Kner P, Chhun BB, Griffis ER, Winoto L, Gustafsson MGL. Super-resolution video microscopy of live cells by structured illumination. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):339–42. [5] Heintzmann R, Huser T. Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy. Chem Rev. 2017;117(23):13890–908. [6] Sahl SJ, Hell SW, Jakobs S. Fluorescence nanoscopy in cell biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(11):685–701. [7] Wu Y, Shroff H. Faster, sharper, and deeper: structured illumination microscopy for biological imaging. Nat Methods. 2018;15(12):1011–9. [8] Demmerle J, Innocent C, North AJ, Ball G, Müller M, Miron E, et al. Strategic and practical guidelines for successful structured illumination microscopy. Nat Protoc. 2017;12(5):988–1010. [9] Wen G, Li S, Wang L, Chen X, Sun Z, Liang Y, et al. High-fidelity structured illumination microscopy by point-spread-function engineering. Light: Sci Appl. 2021;10(1):70. [10] Huang X, Fan J, Li L, Liu H, Wu R, Wu Y, et al. Fast, long-term, super-resolution imaging with Hessian structured illumination microscopy. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36(5):451–9. [11] Wicker K. Non-iterative determination of pattern phase in structured illumination microscopy using auto-correlations in Fourier space. Opt Express. 2013;21(21):24692–701. [12] Hoffman DP, Betzig E. Tiled reconstruction improves structured illumination microscopy. bioRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.06.895318. [13] Wen G, Wang L, Chen X, Tang Y, Li S. Frequency–spatial domain joint optimization for improving super-resolution images of nonlinear structured illumination microscopy. Opt Lett. 2021;46(23):5842–5. [14] Ball G, Demmerle J, Kaufmann R, Davis I, Dobbie IM, Schermelleh L. SIMcheck: a toolbox for successful super-resolution structured illumination microscopy. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):15915. [15] Young LJ, Ströhl F, Kaminski CF. A guide to structured illumination TIRF microscopy at high speed with multiple colors. J Vis Exp. 2016;111: e53988. [16] Liang Y, Chen X, Sun Z, Wen G, Chen C, Wang L, et al. High dynamic range structured illumination microscope based on multiple exposures. Front Phys. 2021;9: 648174. [17] Wicker K, Mandula O, Best G, Fiolka R, Heintzmann R. Phase optimisation for structured illumination microscopy. Opt Express. 2013;21(2):2032–49. [18] Müller M, Mönkemöller V, Hennig S, Hübner W, Huser T. Open-source image reconstruction of super-resolution structured illumination microscopy data in ImageJ. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):10980. [19] Křížek P, Lukeš T, Ovesný M, Fliegel K, Hagen GM. SIMToolbox: a MATLAB toolbox for structured illumination fluorescence microscopy. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(2):318–20. [20] Lal A, Shan C, Xi P. Structured illumination microscopy image reconstruction algorithm. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2016;22(4):50–63. [21] Zhou X, Lei M, Dan D, Yao B, Yang Y, Qian J, et al. Image recombination transform algorithm for superresolution structured illumination microscopy. J Biomed Opt. 2016;21(9): 096009. [22] Cao R, Chen Y, Liu W, Zhu D, Kuang C, Xu Y, et al. Inverse matrix based phase estimation algorithm for structured illumination microscopy. Biomed Opt Express. 2018;9(10):5037–51. [23] Perez V, Chang BJ, Stelzer EHK. Optimal 2D-SIM reconstruction by two filtering steps with Richardson-Lucy deconvolution. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):37149. [24] Smith CS, Slotman JA, Schermelleh L, Chakrova N, Hari S, Vos Y, et al. Structured illumination microscopy with noise-controlled image reconstructions. Nat Methods. 2021;18(7):821–8. [25] Karras C, Smedh M, Förster R, Deschout H, Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Heintzmann R. Successful optimization of reconstruction parameters in structured illumination microscopy – a practical guide. Opt Commun. 2019;436:69–75. [26] Chu K, McMillan PJ, Smith ZJ, Yin J, Atkins J, Goodwin P, et al. Image reconstruction for structured-illumination microscopy with low signal level. Opt Express. 2014;22(7):8687–702. [27] Zhao W, Zhao S, Li L, Huang X, Xing S, Zhang Y, et al. Sparse deconvolution improves the resolution of live-cell super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Nat Biotechnol. 2022;40(4):606–17. [28] Jin L, Liu B, Zhao F, Hahn S, Dong B, Song R, et al. Deep learning enables structured illumination microscopy with low light levels and enhanced speed. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1934. [29] Christensen CN, Ward EN, Lu M, Lio P, Kaminski CF. ML-SIM: universal reconstruction of structured illumination microscopy images using transfer learning. Biomed Opt Express. 2021;12(5):2720–33. [30] Qiao C, Li D, Guo Y, Liu C, Jiang T, Dai Q, et al. Evaluation and development of deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy. Nat Methods. 2021;18(2):194–202. [31] Dan D, Wang Z, Zhou X, Lei M, Zhao T, Qian J, et al. Rapid image reconstruction of structured illumination microscopy directly in the spatial domain. IEEE Photonics J. 2021;13(1):1–11. [32] Wang Z, Zhao T, Hao H, Cai Y, Feng K, Yun X, et al. High-speed image reconstruction for optically sectioned, super-resolution structured illumination microscopy. Adv Photonics. 2022;4(2): 026003. [33] Tu S, Liu Q, Liu X, Liu W, Zhang Z, Luo T, et al. Fast reconstruction algorithm for structured illumination microscopy. Opt Lett. 2020;45(6):1567–70. [34] Neil MAA, Juskaitis R, Wilson T. Method of obtaining optical sectioning by using structured light in a conventional microscope. Opt Lett. 1997;22(24):1905–7. [35] Thomas B, Momany M, Kner P. Optical sectioning structured illumination microscopy with enhanced sensitivity. J Opt. 2013;15(9): 094004. [36] O’Holleran K, Shaw M. Optimized approaches for optical sectioning and resolution enhancement in 2D structured illumination microscopy. Biomed Opt Express. 2014;5(8):2580–90. [37] Stallinga S, Radmacher N, Delon A, Enderlein J. Optimal transfer functions for bandwidth-limited imaging. Phys Rev Research. 2022;4(2): 023003. [38] Wen G, Li S, Liang Y, Wang L, Zhang J, Chen X, et al. Supplementary Code for direct-SIM. figshare. 2022. https://opticapublishing.figshare.com/s/6b7daa9f15e01de4e952. [39] Hüpfel M, Kobitski AY, Zhang W, Nienhaus GU. Wavelet-based background and noise subtraction for fluorescence microscopy images. Biomed Opt Express. 2021;12(2):969–80. [40] Culley S, Albrecht D, Jacobs C, Pereira PM, Leterrier C, Mercer J, et al. Quantitative mapping and minimization of super-resolution optical imaging artifacts. Nat Methods. 2018;15(4):263–6. [41] Markwirth A, Lachetta M, Mönkemöller V, Heintzmann R, Hübner W, Huser T, et al. Video-rate multi-color structured illumination microscopy with simultaneous real-time reconstruction. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4315. [42] Shabani H, Doblas A, Saavedra G, Preza C. Optical transfer function engineering for a tunable 3D structured illumination microscope. Opt Lett. 2019;44(7):1560–3. [43] Manton JD, Ströhl F, Fiolka R, Kaminski CF, Rees EJ. Concepts for structured illumination microscopy with extended axial resolution through mirrored illumination. Biomed Opt Express. 2020;11(4):2098–108. [44] Turcotte R, Liang Y, Tanimoto M, Zhang Q, Li Z, Koyama M, et al. Dynamic super-resolution structured illumination imaging in the living brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:9586–91. [45] Xu K, Zhong G, Zhuang X. Actin, spectrin, and associated proteins form a periodic cytoskeletal structure in axons. Science. 2013;339(6118):452–6. [46] Sahl SJ, Balzarotti F, Keller-Findeisen J, Leutenegger M, Westphal V, Egner A, et al. Comment on “extended-resolution structured illumination imaging of endocytic and cytoskeletal dynamics.” Science. 2016;352(6285):527. [47] Ward EN, Hecker L, Christensen CN, Jacob RL, Meng L, Luca M, et al. Machine learning assisted interferometric structured illumination microscopy for dynamic biological imaging. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7836. [48] Qian J, Cao Y, Bi Y, Wu H, Liu Y, Chen Q, Zuo C. Structured illumination microscopy based on principal component analysis. eLight. 2023;3(1):4. [49] Qiao C, Li D, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liu K, Liu C, et al. Rationalized deep learning super-resolution microscopy for sustained live imaging of rapid subcellular processes. Nat Biotechnol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01471-3. [50] Gao P, Yuan C. Resolution enhancement of digital holographic microscopy via synthetic aperture: a review. Light: Adv Manuf. 2022;3(1):105–20.








 下载:
下载: